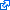
The paragraphs below are positioned using the default position value: static. They are laid out one after the other with normal top and bottom margins creating the space between them. This is the normal flow of the document and is what occurs by default if you don't adjust the CSS in any way (I only added borders to display each paragraph's box). "Normal flow" applies to any element that does not specify position:absolute or fixed and is not floated.
Static elements ignore any top, bottom, left or right positioning declarations.
This is the first paragraph of the positioning demo. The objective of the next few pages is to demonstrate the difference between
the four position property values: static, relative, absolute and fixed. The key to working with the position property
is to understand that every element is positioned with respect to another element; which element that is can be changed
by altering the value of the position property.
This is the second paragraph of the positioning demo. The objective is to demonstrate the difference between the four position property values: static, relative, absolute and fixed.
This is the third paragraph of the positioning demo. The objective is to demonstrate the difference between the four position property values: static, relative, absolute and fixed.
This is the fourth paragraph of the positioning demo. The objective of the next few pages is to demonstrate the difference between the four position property values: static, relative, absolute and fixed. This is the fourth paragraph of the positioning demo. The objective of the next few pages is to demonstrate the difference between the four position property values: static, relative, absolute and fixed. This is the fourth paragraph of the positioning demo. The objective of the next few pages is to demonstrate the difference between the four position property values: static, relative, absolute and fixed.